- Home
- About us
- Products
- square steel pipe
- rectangular steel pipe
- round steel pipe
- shaped tube
- LSAW steel pipe
- zinc aluminium magnesium coating steel pipe
- galvanized steel pipe
- ERW steel pipe
- seamless steel pipe
- spiral steel pipe
- LINE PIPE&OCTG
- stainless steel pipe
- steel coil
- steel plate
- ship building steel pipe
- photovoltaic bracket
- steel profile
- u channel
- Faqs
- News
- Certificate
- Contact us
How to produce Hot Dipped Galvanized steel pipe?
hot dip galvanized steel pipe manufacturing process
Hot dip galvanizing (English name: Galvanizing, also known as hot-dip galvanizing or hot-dip galvanizing, is an effective method of metal corrosion prevention, mainly used on metal structural facilities in various industries.
It is to immerse the rust removed steel components into a molten zinc solution at around 500 ℃, so that a zinc layer adheres to the surface of the steel components, thereby achieving the purpose of corrosion prevention. Hot dip coating
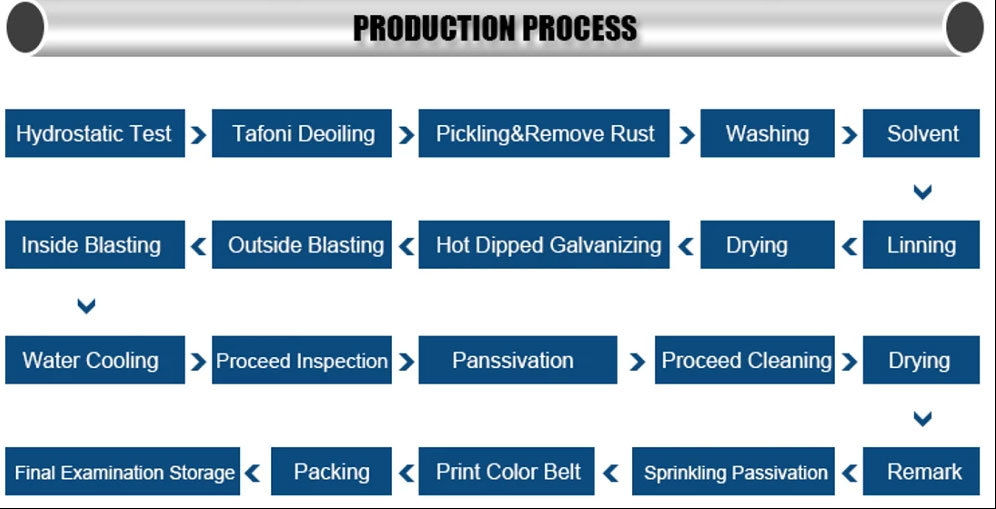
Feng process flow: finished product pickling: water washing, adding cooking solution, drying, hanging mirror: cooling, chemical cleaning and polishing: hot coating completion, hot mixing is developed from the ancient hot plating method, which has a history of more than 170 years. In the past thirty years, with the rapid development of cold-rolled steel strips, the thermal cracking industry has been able to achieve large-scale production
Model development.
Hot dip galvanizing production process
Loading, acid washing, water washing, solvent drying, hot-dip galvanizing, internal and external blowing, rolling, marking, passivation, inspection, packaging
Hot-dip galvanizing steps
The hot-dip galvanizing of steel pipes adopts the mechanical principle of dialing in, pressing down, spiraling, pulling out and lifting in a fully immersed semi-automatic galvanizing method with a toothed disc to complete the hot-dip galvanizing process.
1. Process parameter control: the temperature of the zinc liquid should be controlled between 440-460℃; the zinc dipping time should be controlled between 30-60 seconds; add aluminum (the aluminum content of the zinc liquid surface is 0.01-0.02%)
2. The zinc ingot used should be the national standard Zn0-3 zinc ingot.
3. Regularly maintain and control the reliability of the pull-in, press-down spiral, pull-out and lifting device, strengthen the lubrication of the cylinder, adjust the height and angle of the galvanized pipe distributor, and adjust the equipment to the best state.
4. The placement of the proximity switch should be accurate; the thermocouple wire and the meter should be used with the same model, otherwise, the temperature error will be large, and the protective sleeve of the thermocouple should be checked and replaced frequently.
The operator at the operating table should adjust the speed manually according to the operation of the equipment in front of the furnace and the hand gesture command to prevent the pipe from getting stuck.
6. The tools used by the furnace workers should be preheated before use to prevent zinc splashing and injuring people; check frequently whether there are steel pipes falling into the pot, and clear them out if necessary; adjust the equipment in time to avoid pipe jams to ensure the safety of the equipment.
The zinc ingot should be placed vertically against the wall of the zinc pot and slowly drawn down to avoid impact damage to the zinc pot and splashing a large amount of zinc to injure people; iron substances are strictly prohibited in the zinc liquid. 7. When adding zinc to the zinc pot, the zinc ingot should be preheated first. When adding zinc, it is not allowed to add zinc in bundles. No more than five pieces of zinc should be added each time to prevent the generation of a large amount of zinc slag. 8. When melting zinc, it should be heated slowly, and it should not be burned quickly, otherwise it will damage the life of the galvanizing pot, and a large amount of zinc vapor will evaporate. If this harmful gas is inhaled excessively by the human body, it will cause a disease called "foundry fever". During the zinc melting process, once the zinc has reached a high temperature, you must not move the zinc block by hand to avoid burns. You should use appropriate tools to move it.
9. Clean the zinc ash on the surface of the zinc liquid regularly. When scraping the ash, you should gently scrape it on the surface of the zinc liquid with a scraper. Do not stir it too hard to avoid the zinc ash flying. The scraper should not collide with the steel pipe that is being zinced or discharged to avoid rolling and causing personal accidents or equipment accidents. 10. The zinc blocks, broken zinc, zinc brought out during galvanizing, and zinc flowing out of the steel pipe on the ground in front of the furnace should be recovered and returned to the pot at any time to reduce the heat loss of the zinc pot.
11. When adding aluminum ingots to the surface of the zinc liquid, be sure to move it back and forth several times to ensure that the aluminum content on the surface of the zinc liquid is uniform.
12. In order to facilitate slag removal and zinc extraction, 20 tons of lead should be placed inside the zinc pot.
13. When scooping slag, the slag scoop machine must be preheated. The zinc slag should be stored in large and small pieces. The slag temperature should be controlled above 455℃. Special tools must be used when using the swing slag grabber. Keep your feet 1 meter away from the zinc pot and stand in a T shape. 14. The hot-dip galvanizing process has strict requirements, so in the hot-dip galvanizing production process, you must do enough work. That is to say, the more roots or tonnage per unit time, the lower the cost, and vice versa.
