- Home
- About us
- Products
- square steel pipe
- rectangular steel pipe
- round steel pipe
- shaped tube
- LSAW steel pipe
- zinc aluminium magnesium coating steel pipe
- galvanized steel pipe
- ERW steel pipe
- seamless steel pipe
- spiral steel pipe
- LINE PIPE&OCTG
- stainless steel pipe
- steel coil
- steel plate
- ship building steel pipe
- photovoltaic bracket
- steel profile
- u channel
- Faqs
- News
- Certificate
- Contact us
How to produce Electrical Resistance Weld Pipe-ERW?
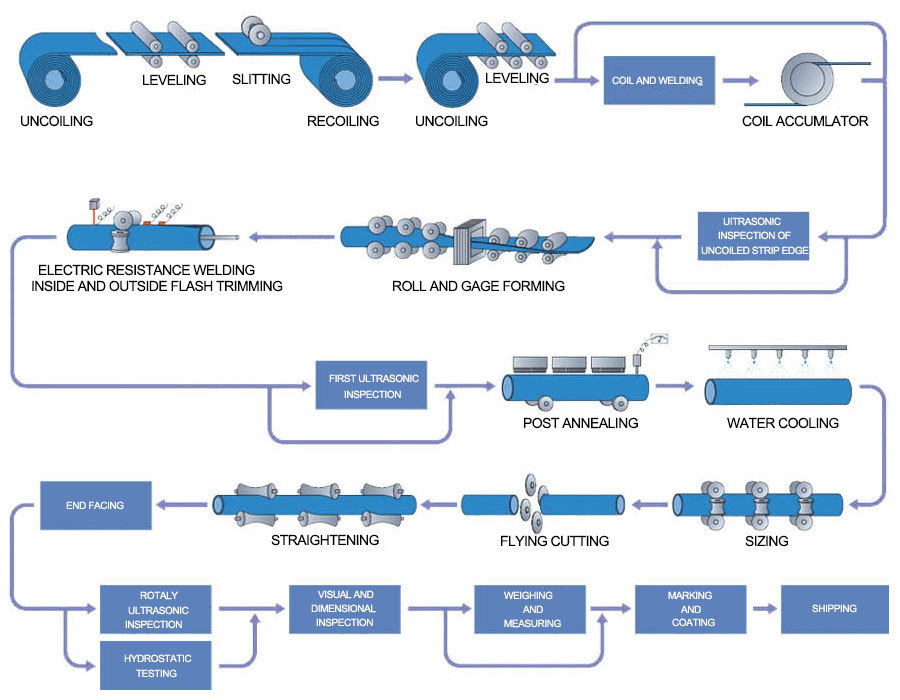
Electric Resistance Welded Pipe (ERW) is a steel pipe manufactured by high-frequency resistance welding technology. This production method is known for its high efficiency, high quality and flexibility, and is widely used in oil and gas transportation, building structures, machinery manufacturing and other fields. The following are the main production process steps of electric resistance welded pipe:
1. Raw material preparation
Selection of strip steel or steel plate: Select the appropriate strip steel or steel plate as the raw material according to the required final product specifications.
Pretreatment: Clean, straighten and flatten the strip steel to ensure that the surface is clean and free of impurities to ensure the quality of subsequent processes.
2. Forming
Curling: The strip steel is gradually bent into a circular cross-section through a series of rollers. The design of each roller is precisely calculated to ensure that the strip steel can be smoothly formed into the required diameter and wall thickness.
Pre-bending: During the forming process, the edges of the strip steel are usually pre-bent to make them easier to butt and weld.
3. Welding
High-frequency resistance welding: This is the core step in the production of ERW pipes. The resistance heat generated by high-frequency current is used to melt the edges of the strip steel, so that the edges on both sides are fused under pressure to form a weld. The process does not require additional filler materials, ensuring the consistency of the weld joint with the parent material.
High-frequency power supply: Provides sufficient power to generate high-frequency current.
Induction coil: Surrounds the area to be welded and heats the edge of the strip to the melting point by electromagnetic induction.
Squeeze roller: Apply appropriate pressure to make the molten edges tightly bonded to form a solid weld.
4. Sizing and cooling
Sizing machine adjusts the size: After welding, the steel pipe passes through the sizing machine to further adjust its outer diameter and inner diameter to ensure that the dimensional accuracy meets the standard requirements.
Natural cooling or forced cooling: The steel pipe can be cooled naturally or accelerated by air cooling, water cooling, etc., depending on the speed of the production line and the final use of the product.
5. Inspection and testing
Appearance inspection: Visually inspect the surface of the steel pipe for obvious defects such as cracks, pores, etc.
Dimension measurement: Use tools such as calipers and micrometers to measure key dimensions such as diameter and wall thickness of the steel pipe.
Non-destructive testing: Use ultrasonic testing (UT), magnetic particle testing (MT), penetrant testing (PT) and other methods to detect potential defects inside and on the surface.
Water pressure test: Carry out water pressure test on finished steel pipes to verify their sealing and pressure resistance.
6. Finishing and Packaging
End processing: Cut, chamfer or perform other necessary processing on both ends of the steel pipe according to customer needs.
Painting and marking: To prevent corrosion during transportation and storage, the surface of the steel pipe may need to be painted or galvanized, and product information labels may be stamped.
Packaging and delivery: Qualified products are packaged according to customer requirements and prepared for delivery.
Key technologies and equipment
High-frequency welding equipment: including high-frequency power supply, induction coil and extrusion roller, is the key to achieving efficient and high-quality welding.
Automation control system: Modern ERW production lines are equipped with advanced automation control systems that can monitor and adjust various process parameters in real time to ensure the stability and consistency of production.
Quality inspection system: From raw materials to finished products, a strict quality inspection system is equipped throughout the process to ensure that each steel pipe meets high standards.
Advantages
High efficiency: Compared with seamless steel pipes, ERW pipes are produced faster and at lower costs.
High quality: By precisely controlling welding parameters, high-strength and stable performance welds can be obtained.
Flexibility: The production line can be quickly adjusted according to market demand to produce steel pipes of different specifications and lengths.
Environmentally friendly: Since no additional welding materials are required, waste generation is reduced, which is in line with the concept of green manufacturing.
Application areas
ERW pipes are widely used in many industries due to their excellent mechanical properties and economy:
Oil and gas transportation: long-distance oil and gas pipelines, submarine laying, etc.
Building structures: infrastructure construction such as high-rise buildings, bridges, tunnels, etc.
Machinery manufacturing: automotive parts, engineering machinery, etc.
Water conservancy projects: irrigation channels, drainage networks, etc.
Chemical equipment: piping systems exposed to corrosive chemicals.
Summary
The production process of electric resistance welded pipe (ERW) combines advanced forming and welding technologies, which can improve production efficiency while ensuring product quality. With the advancement of technology, the application range of ERW pipes continues to expand, becoming the preferred material in many engineering projects. If you have more specific questions about ERW pipes or need further help, please feel free to let me know. I hope the above information can provide you with valuable reference.
