- Home
- About us
- Products
- square steel pipe
- rectangular steel pipe
- round steel pipe
- shaped tube
- LSAW steel pipe
- zinc aluminium magnesium coating steel pipe
- galvanized steel pipe
- ERW steel pipe
- seamless steel pipe
- spiral steel pipe
- LINE PIPE&OCTG
- stainless steel pipe
- steel coil
- steel plate
- ship building steel pipe
- photovoltaic bracket
- steel profile
- u channel
- Faqs
- News
- Certificate
- Contact us
rounded square tube| Low carbon steel

- group name
- square steel pipe
- Min Order
- 5 ton
- brand name
- Yuantai Derun Steel Pipe Manufacturing Group
- model
- Square Tubes Round Corners
- Nearest port for product export
- XINGANG PORT TIANJIN CHINA, TANGSHAN CHINA, SHANGHAI CHINA, DALIAN PORT
- Delivery clauses under the trade mode
- FOB, CFR, CIF, EXW
- Acceptable payment methods
- T/T, L/C, Cash
- update time
- Mon, 22 Dec 2025 22:55:44 GMT
Paramtents
Thickness 0.5- 60 mm
OD(Outer diameter) 10*10-1000*1000mm
Certification CE,LEED,BV,PHD&EPD,BC1,EN 10210,EN10219,ISO9000
Tolerance as required
Length 0.5-26.5M according to client requirement
Standards ASTM A500/A501,EN10219,EN10210
Materials Gr.A, Gr.B, Gr.C, S235, S275, S355,S420,S460, A36,
Delivery Time 7-30 Days
Packging & Delivery
-
Min Order5 ton
Briefing
Detailed
Rounded Square Tube
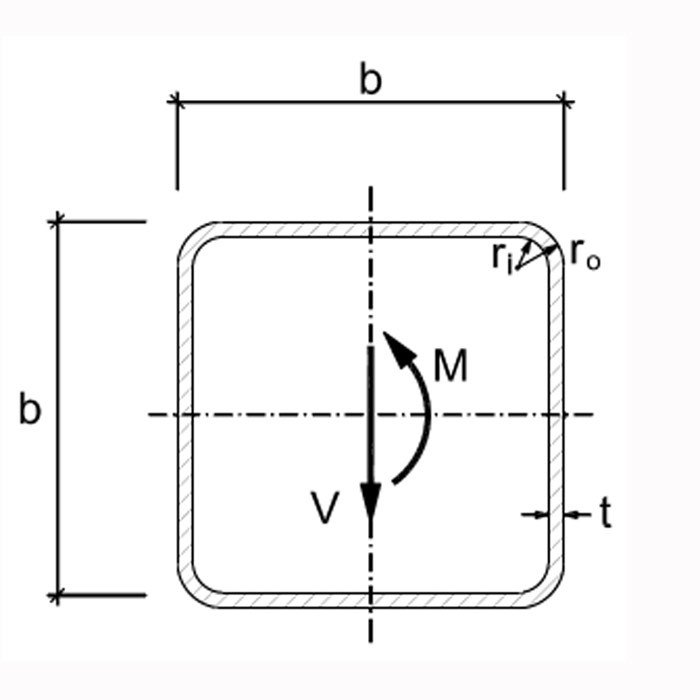
Steel Square Tube / Tubing Radius Corner
Complete Square Tubes Round Corners Sizes
Steel Square Radius Tube Coating
Added Service
Hot Finished
Sometimes, in order to better remove the stress inside the rounded square steel, customers need to perform heat treatment on the steel pipe. At Yuantai Derun, we have two heat treatment methods: tube body four corner heating and heating furnace heating, both of which can meet the requirements of removing internal stress. If you also have concerns about stress, please contact us immediately.
Punching

Free Rounded Square Tube Samples For You
Application
Project



